European theatre of World War II
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2021) |
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat[nb 22] during World War II. It saw heavy fighting across Europe for almost six years, starting with Germany's invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 and ending with the Western Allies conquering most of Western Europe, the Soviet Union conquering most of Eastern Europe including the German capital Berlin, and Germany's unconditional surrender on 8 May 1945[nb 23] although fighting continued elsewhere in Europe until 25 May. On 5 June 1945, the Berlin Declaration proclaiming the unconditional surrender of Germany to the four victorious powers was signed. The Allied powers fought the Axis powers on two major fronts (Eastern Front and Western Front), but there were other fronts varying in scale from the Italian campaign (the 3rd largest campaign in Europe), to the Polish Campaign, as well as in a strategic bombing offensive and in the adjoining Mediterranean and Middle East theatre.
Preceding events
[edit]Germany was defeated in World War I, and the Treaty of Versailles placed punitive conditions on the country, including significant financial reparations, the loss of territory (some only temporarily), war guilt, military weakening and limitation, and economic weakening. Germany was "humiliated" in front of the world and had to pay very large war reparations. Many Germans blamed their country's post-war economic collapse on the treaty's conditions and these resentments contributed to the political instability, which made it possible for Adolf Hitler and his Nazi Party to come to power.
After Hitler took Germany out of the League of Nations, Mussolini of Fascist Italy and Hitler formed the Rome-Berlin axis, under a treaty known as the Pact of Steel. Later, the Empire of Japan, under the government of Hideki Tojo, would also join as an Axis power. Japan and Germany had already signed the Anti-Comintern Pact in 1936, to counter the perceived[citation needed] threat of the communism of the Soviet Union. Other smaller powers also later joined the Axis throughout the war.
Outbreak of war in Europe
[edit]Germany and the Soviet Union were sworn enemies, but following the Munich Agreement, which effectively handed over Czechoslovakia (a French and Soviet ally, and the only remaining presidential democracy in Central Europe) to Germany, political realities allowed the Soviet Union to sign a non-aggression pact (the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact) including a secret clause partitioning Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia and Finland between the two spheres of influence.
Full-scale war in Europe began at dawn on 1 September 1939, when Germany used so-called Blitzkrieg tactics and military strength to invade Poland, to which both the United Kingdom and France had pledged protection and independence guarantees. On 3 September 1939, Britain and France declared war on Germany, and other allies soon followed. The British Expeditionary Force was sent to France; however, neither French nor British troops gave any significant assistance to the Poles during the entire invasion, and the German–French border, excepting the Saar Offensive, remained mostly calm. This period of the war is commonly known as the Phoney War.
On 17 September the Soviet forces joined the invasion of Poland, although remaining neutral with respect to Western powers. The Polish government evacuated the country for Romania. Poland fell within five weeks, with its last large operational units surrendering on 6 October after the Battle of Kock. As the Polish September Campaign ended, Hitler offered Britain and France peace on the basis of recognition of German European continental dominance. On 12 October the United Kingdom formally refused.
Despite the quick campaign in the east, along the Franco-German frontier the war settled into a quiet period. This relatively non-confrontational and mostly non-fighting period between the major powers lasted until Germany launched an invasion on 10 May 1940.
Germany and the USSR partition Northern Europe
[edit]
Several other countries were drawn into the conflict at this time. After 28 September 1939, the Soviet government presented the governments of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania with ultimatums threatening military invasion, thus compelling the three small nations to conclude mutual assistance pacts which gave the Soviets the right to establish military bases there. The Soviet Union issued similar demands to Finland in October 1939 but these were rejected, leading to the Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November, starting the Winter War.
The Soviet Union did not accomplish its goal of annexing Finland.[28] In the Moscow Peace Treaty of April 1940, Finland ceded 9% of its territory, including parts of Karelia and Salla. The Finns were embittered over having lost more land in the peace than on the battlefields, and over the perceived lack of world sympathy.
In the rest of Scandinavia, Germany invaded Denmark and Norway in April 1940, and in response, Britain occupied the Faroe Islands (a Danish territory) and invaded and occupied Iceland (a sovereign nation with the King of Denmark as its monarch). Sweden was able to remain neutral.
The Baltic Republics were occupied by the Soviet army in June 1940, and formally annexed to the Soviet Union in August 1940.
War comes to the West
[edit]
On 10 May 1940 the Phoney War ended with a sweeping German invasion of the neutral Low Countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg, and into France bypassing the French fortifications of the Maginot Line along the border with Germany. After overrunning the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg, Germany turned against France, entering the country through the Ardennes on 13 May – the French had left this area less well defended, believing its terrain to be impassable for tanks and other vehicles. Most Allied forces were in Flanders, anticipating a re-run of the World War I Schlieffen Plan, and were cut off from the French mainland. As a result of this, as well as the superior German communications and tactics, the Battle of France lasted only six weeks; far shorter than what virtually all pre-war Allied thought could have conceived. On 10 June Italy declared war on both France and the United Kingdom but did not gain any significant success in this campaign. The French government fled Paris, and soon, France surrendered on 22 June. In order to further the humiliation of the French people and the country itself, Hitler arranged for the surrender document to be signed in the Forest of Compiègne, in the same railway coach where the German surrender had been signed in 1918. The surrender divided France into two major parts; the northern part under German control, and a southern part under French control, based at Vichy and referred to as Vichy France, a rump state friendly to Germany. Many French soldiers, as well as those of other occupied countries, escaped to Britain. General de Gaulle proclaimed himself the legitimate leader of Free France and vowed to continue to fight. Following the unexpectedly swift victory, Hitler promoted twelve generals to the rank of field marshal during the 1940 Field Marshal Ceremony.
Vyacheslav Molotov, the Foreign Policy Minister of the USSR, which was tied with Soviet–German non-aggression treaty, congratulated the Germans:
We hand over the most cordial congratulations by the Soviet government on the occasion of splendid success of German Wehrmacht. Guderian's tanks broke through to the sea near Abbeville, powered by Soviet fuel, the German bombs, that razed Rotterdam to the ground, were filled with Soviet pyroxylin, and bullet cases, which hit the British soldiers retreating from Dunkirk, were cast of Soviet cupronickel alloy...[29][unreliable source?][dubious – discuss]
On 24 April 1941 the USSR gave full diplomatic recognition to the Vichy government situated in the non-occupied zone in France.[30]
Thus, the Fall of France left Britain and the Commonwealth to stand alone. The British Prime Minister, Neville Chamberlain, resigned during the battle and was replaced by Winston Churchill. Much of Britain's army escaped capture from the northern French port of Dunkirk, where hundreds (if not thousands) of tiny civilian boats were used to ferry troops from the beaches to the waiting warships. There is much debate over whether German Panzer divisions could have defeated these soldiers alone if they had pressed forward, since the tank divisions were overextended and would have required extensive refitting; in any case, Hitler elected to follow the advice of the leader of German air forces Hermann Göring and allow the Luftwaffe alone to attack the Allied forces until German infantry was able to advance, giving the British a window for the evacuation. Later, many of the evacuated troops would form an important part and the centre of the army that landed at Normandy on D-Day.
The British rejected several covert German attempts to negotiate peace. Germany massed their air force in northern German-occupied France to prepare the way for a possible invasion, code-named Operation Seelöwe ("Sea Lion"), deeming that air superiority was essential for the invasion. The operations of the Luftwaffe against the Royal Air Force became known as the Battle of Britain. Initially, the Luftwaffe concentrated on destroying the RAF on the ground and in the air. They later switched to bombing major and large industrial British cities in the Blitz, in an attempt to draw RAF fighters out and defeat them completely. Neither approach was successful in reducing the RAF to the point where air superiority could be obtained, and plans for an invasion were suspended by September 1940.
During the Blitz, all of Britain's major industrial, cathedral, and political sites were heavily bombed. London suffered particularly, being bombed each night for several months. Other targets included Birmingham and Coventry, and strategically important cities, such as the naval base at Plymouth and the port of Kingston upon Hull. With no land forces in direct conflict in Europe, the war in the air attracted worldwide attention even as sea units fought the Battle of the Atlantic and a number of British commando raids hit targets in occupied Europe. Churchill famously said of the RAF personnel who fought in the battle: "Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few".
Air war
[edit]This section needs expansion with: aerial warfare on the Eastern Front and Soviet-based air operations. You can help by adding to it. (May 2013) |

The air war in the European theatre commenced in 1939.
Pre-war expectations that "The bomber will always get through" assumed that waves of bombers hitting enemy cities would cause mass panic and the rapid collapse of the enemy. As a result, the Royal Air Force had built up a large strategic bomber force. By way of contrast, Nazi German air force doctrine was almost totally dedicated to supporting the army. Therefore, German bombers were smaller than their British equivalents, and Germany never developed a fully successful heavy bomber equivalent to the British Avro Lancaster or American Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, with only the similarly sized Heinkel He 177A placed into production and made operational for such duties with the Luftwaffe in the later war years.
Initial German bomber attacks against the UK were targeted at the RAF's airfields during the Battle of Britain; from 7 September 1940 until 10 May 1941 the targets were British towns and cities in "The Blitz".
Following the abandonment of any idea of invasion of the UK, most of the strength of the Luftwaffe was diverted to the war against the Soviet Union leaving German cities vulnerable to British and later American air bombings. Great Britain was used by the U.S and other Allied forces as a base from which to begin the D-Day landings in June 1944 and the liberation of Nazi-occupied Western Europe. Nevertheless, German raids continued on British cities albeit on a smaller and less destructive scale for the rest of the war, and later the V1 Flying Bomb and V-2 ballistic missiles were both used against Britain. However, the balance of bomb tonnage being dropped shifted greatly in favour of the RAF as RAF Bomber Command gained in strength.
British bombing by day resulted in too many losses and too few results; as a result the British operated by night while building up their strategic force with larger bombers. By 1942, Bomber Command could put 1,000 bombers over one German city.
During the initial raids of Operation Barbarossa the Luftwaffe wiped out the majority of the Soviet air forces. The Soviets would only regain their air wing later in the war with the help of the Allies, aircraft being delivered mainly by arctic convoys.
From 1942 onwards, the efforts of Bomber Command were supplemented by the Eighth Air Force of the United States Army Air Forces, U.S. Army Air Forces units being deployed to England to join the assault on mainland Europe on 4 July 1942. Bomber Command raided by night and the US forces by day. The "Operation Gomorrah" raids on Hamburg (24–29 July 1943) caused a firestorm, leading to massive destruction and loss of life.
On 14 February 1945, a raid on Dresden produced one of the most devastating fires in history. A firestorm was created in the city, and between 18,000 and 25,000 people were killed.[31][32][33] Only the Hamburg attack, the 9–10 March 1945 firebombing of Tokyo and the nuclear attacks on Hiroshima (6 August 1945) and Nagasaki (9 August 1945) killed more people through a single attack.
Mediterranean and Balkan campaigns
[edit]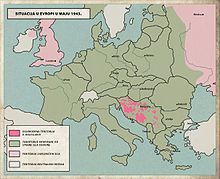
The Mediterranean and Middle East theatre was a major theatre of operations during the Second World War. The vast size of this theatre included the fighting between the Allies and Axis in Italy, the Balkans, Southern Europe, Malta, North Africa and the Middle East.
Prior to the war Italy had invaded Albania and officially annexed it. Mussolini's regime declared war on Britain and France on 10 June 1940, and invaded Greece on 28 October. However, Italian forces were unable to match the Nazi successes in northwest Europe; in fact, it was not until German intervention that Greece was overrun by the Axis powers. While the Greek campaign was underway, German forces, supported by the Italians, Hungarians and the Bulgarians simultaneously invaded Yugoslavia. After the mainland was conquered, Germany invaded Crete in what is known as the Battle of Crete. With the Balkans secure, Germany and its allies attacked the Soviet Union in the largest land operation in history. The Balkans campaign delayed this invasion,[citation needed] and subsequent resistance movements in Albania, Yugoslavia and Greece tied up valuable Axis forces.[citation needed] This provided much needed and possibly decisive relief for the Soviets.[citation needed]
Fighting in Southern Europe did not resume until Axis forces were defeated in North Africa. Following the Axis defeat in Africa, Allied forces invaded Italy and during a prolonged campaign fought their way north through Italy. The invasion of Italy resulted in the nation switching sides to the Allies and the ousting of Mussolini. Despite this coup, Fascists and occupying German forces retained possession of the northern half of Italy. In the northern part of Italy, the occupying Germans installed Mussolini as the head of the new fascist republican government, the Italian Social Republic or RSI to show that the Axis forces were still in power there and a force to be dealt with. However, Mussolini and his Fascists were now puppet rulers under their German patrons.
On the opposite side of the Adriatic Sea the Allied (and mostly pro-Soviet) National Liberation Army of Yugoslavia, which got some supplies and assistance from Western Allies, battled the Axis powers. In late 1944 it was joined by the advancing Soviet Army and proceeded to push the remaining German forces out of the Balkans.
By April 1945, German forces were retreating on all fronts in northern Italy and occupied Yugoslavia, following continuous Allied attacks. The campaign and the fighting in the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre came to an end on 29 April. On 2 May in Italy, Field Marshal Heinrich von Vietinghoff, the commander-in-chief of all German forces in the country surrendered to Field Marshal Harold Alexander, the supreme commander of all Allied forces in the Mediterranean area. In a preview of the Cold War, fighting continued in Greece where a civil war broke out and lasted until the end of 1949 when Greek government troops, aided by the US and Britain, defeated the communist guerrillas supported by Marshal Tito and USSR.
Eastern Front
[edit]Initial Soviet retreat
[edit]
On 22 June 1941, Germany launched the invasion of the Soviet Union, code-named Operation Barbarossa.[34] This invasion, the biggest in recorded history, started the bloodiest conflict in world history: the Axis–Soviet War, also known as the Eastern Front. It is generally accepted as being the most lethal conflict in human history, with over 30 million dead as a result. It involved more land combat than all other World War II theatres combined.
On the very night of the invasion Soviet troops received a directive undersigned by Marshal Timoshenko and General of the Army Georgi Zhukov that commanded: "do not answer to any provocations" and "do not undertake any actions without specific orders". The early weeks of the invasion were devastating for the Soviet Army. Enormous numbers of Soviet troops were encircled in pockets and fell into Nazi German hands. In addition to German troops, Italian, Hungarian, Romanian and Finnish troops were also involved in the campaign. Finland initially declared neutrality; however, with both German and Soviet troops on its soil, Finland was prepared to join forces with Germany when the Soviet Union attacked Finland on 25 June. The following conflict from 1941 to 1944 is sometimes referred to as the Continuation War, as in the continuation of the Winter War. Spain, under the fascist dictator Francisco Franco, immediately offered military assistance to the Axis effort by sending volunteers known as the Blue Division to the Eastern front.
Operation Barbarossa suffered from several fundamental flaws. The most serious of these was the logistical situation of the attack. The sheer vastness of the distances in the Soviet Union meant that Germany could only advance so far before outrunning their supply chains. A crucial mistake on the part of Germany was that the timetable for Barbarossa was planned with the assumption that the Soviets would collapse before the onset of winter. By the time the German attack froze to a halt before the city of Moscow on 5 December 1941, it literally could not go any further. There simply were not enough supplies reaching the front to conduct proper defensive operations, let alone a proper offense.
During their long retreat, the Soviets employed a scorched earth policy. They burned crops and destroyed utilities as they withdrew before Germany's advance, which contributed to the logistical problems that Germany experienced. More importantly for them, the Soviets also succeeded in a massive and unprecedented removal of their industrial resources from the threatened war zone to protected areas further east.
The extension of the campaign beyond the length that Germany expected meant that the German Army suffered hundreds of thousands of casualties in winter conditions and from the counterattacks of Soviet units.
Even with their advance having ground to a halt due to a lack of supplies and the onset of winter, Germany had conquered a vast amount of territory, including two-fifths of the Soviet economy. Dislodging them proved difficult and eventually cost the Soviet Union dearly.
A few months after the invasion began, German troops came to southern approaches to Leningrad and laid siege to the city (known as the Siege of Leningrad), which was also blocked from the north by Finnish forces. Finland's Commander-in-Chief Mannerheim had halted at the River Svir and refrained from attacking the city. Hitler had ordered that the city of Leningrad must "vanish from the surface of the earth", with its entire population exterminated. Rather than storming the city, the Wehrmacht was ordered to blockade Leningrad so as to starve the city to death, while attacking it with bombers and artillery. About one million civilians died in the Leningrad siege – 800,000 by starvation. The siege lasted for 872 days. The only overland way into the city was possible during the winter, across the frozen Lake Ladoga, between the German and Finnish lines.
Case Blue and the Battle of Stalingrad
[edit]
Germany wanted to capture Stalingrad to cut the Soviet's transportation hub with southern Russia, which would let the Germans take the Caucasus region and its oil fields. It would also be a symbolic victory to capture the city that included Joseph Stalin's name. On 5 April, 1942, Hitler confirmed Case Blue, which planned to destroy the Soviet forces in the south, and then afterwards, go north to take Moscow or finish taking the Caucasus. On 28 June, Fedor von Bock's Army Group South began the operation. On 9 July, Hitler amended Operation Blue to involve the taking of Stalingrad and the Caucasus at the same time. Army Group South would be split into Army Group A, led south by Wilhelm List, and Army Group B, led to Stalingrad by Bock. Days later, Bock was replaced by Maximilian von Weichs. The Soviets had faced encirclement until Army Group B split, allowing them to retreat eastwards.[35]

Army Group A captured Rostov-na-Donu and went into the Caucasus in Operation Edelweiss. Army Group B's advance was Operation Fischreiher. Hitler then reassigned the 4th Panzer Army in Army Group B to help out Army Group A. Stalin and the Soviet high command formed the Stalingrad Front of multiple armies: the 21st, 62nd, 63rd, and 64th Armies, as well as the 8th Air Army. He ordered them on 28 July to take "Not One Step Back" and defend Stalingrad. He disallowed the evacuation of civilians from the city, for the purpose of motivating soldiers who would be defending civilians. Hitler then moved the 4th Panzer Army to move north and attack Stalingrad from the south. On the way there, the 4th Panzer Army converged with the 6th Army.[35]
On 23 August, 1942, the Battle of Stalingrad began, as a German spearhead attacked the city from the north and the Luftwaffe began bombing. The fighting was some of the most intense of World War II, as the Soviets and Germans fought over blocks and buildings. The Germans pushed the Soviets through the city until they only occupied a strip of the city near the Volga river 15 kilometers long and 3 to 5 kilometers wide. The Soviets on the other side of the river took supply crossings into the city. On 14 October, the Germans fired on a supply crossing, greatly hurting the Soviets. As winter came, the Germans faced heavy losses and fatigue.[35]

From 19 to 23 November, 1942, the Soviets launched Operation Uranus, a large counteroffensive formulated by Zhukov, Aleksandr Vasilevsky, and Nikolai Voronov. It attacked the weak and undefended flanks of the 4th Panzer Army and 6th Army, greatly surprising the Germans. The German high command asked Hitler to allow the 6th Army, which was fighting near the Volga, to join the rest of the German forces in the west of the city, but Hitler told ordered the leader of the 6th Army, Freidrich Paulus, to stay at the Volga. The Luftwaffe made minor deliveries of supplies to the 6th Army.[35]
In mid-December 1942, Hitler created Operation Winter Storm, forming a special army corps led by Erich von Manstein which would help the 6th Army. The operation failed, and Hitler told the troops to fight to the death. On 10 January, 1943, the Soviets began Operation Koltso, which surrounded the 6th Army. On 31 January, Paulus disobeyed Hitler by surrendering, and soon, 22 generals surrendered with him. By 2 February, the remaining 91,000 German men had surrendered. There were more than 800,000 Axis casualties, 1.1 million Soviet casualties, and 40,000 civilian casualties. Many of the surrendering Germans were put in Soviet prison camps.[35]
Battles after Stalingrad
[edit]
On 5 July, 1943, the Germans began Operation Citadel, an assault on a bulge in the Soviet salient around the city of Kursk.[36][37] The bulge went 100 miles west towards the German lines. 900,000 German troops attacked from the north and south, beginning the Battle of Kursk. It was the largest tank battle in history, involving 6,000 tanks among both sides. The Soviets had predicted the attack, and moved their main forces out of the area. They had also placed minefields and antitank defenses, which costed the Germans.[36] On the 9th, the Allies began invading Sicily, and Hitler had to move troops there from the Eastern Front.[37] Meanwhile, the Soviets began a buildup of forces, and on 12 July, they counterattacked. The Soviets' better numbers allowed them to make a larger offensive; they took back Orel on 5 August and Kharkov on 23 August.[36] There were 800,000 Soviet casualties and 200,000 German casualties.[37]
On 24 December, 1943, Nikolai Vatutin's Soviet forces broke out of their salient in Kyiv and soon retook Zhytomyr and Korosten. Throughout 1944, the Germans faced having less troops while needing to defend the same wide frontlines. In January, the Germans' surrounding of Leningrad was weakened. On 4 January, 1944, the Soviets crossed the pre-war Polish borders. Erich von Manstein's German forces slowed Vatutin's progress, but Germany lost many soldiers, and their defensive line across the Eastern Front was weakened. The Soviets used this to capture Lutsk in modern Ukraine on 5 February. In March, the Soviets crossed the Dnieper and Bug rivers, coming near Romania and Hungary. Hitler reinforced his troops in Hungary to stop further Soviet advance into central Europe, and to maintain his control of the Balkans. On 1 April, Zhukov attempted to break through these defenses into Hungary, but was unsuccessful. Later that month, the Soviets regained the Crimea and Odesa, and German troops left Sevastopol. In May, Germany stabilized the Eastern Front, but they were "unstable, both politically and militarily, under the surface."[38]

On 23 June, 1944, the Soviets launched a large counter-offensive, Operation Bagration, against Germany along a 450-mile front across eastern Europe. The Germans expected an offensive from the south and were surprised at the operation's scale. The Soviets were quickly successful, killing thousands within days. After reaching Minsk on 3 July, 100,000 Germans were killed. The way to Poland and Lithuania opened up to the Soviets. Lviv and all of Byelorussia were liberated by the end of July.[39][38] From 22 to 23 July, Madjanek near Lublin, Poland became the first major Nazi concentration camp was liberated by the Allies. The Soviets then liberated Lublin on the 24th.[40] Operation Bagration ended on 19 August, 1944. There were 750,000 Soviet casualties and 360,000 to 670,000 German casualties.[39]
As the Soviets advanced towards Warsaw in July 1944, they had promised aid to the underground resistance in the city, the Home Army, and encouraged them to start an uprising against the occupying Germans. The Home Army attempted to gain control over the city before the Soviets got there. Starting on 1 August, in the Warsaw Uprising, the Poles captured most of the city from a weakened German garrison. On 25 August, the Germans launched a successful and brutal counterattack. The Soviets gave aid to the Home Army on 13 September, but it was too late to significantly help them. The Home Army split into smaller units and continued the uprising, but they were forced to surrender on 2 October. The Germans deported the city's population and razed it. The Soviets had allowed the Germans to suppress the uprising, thus causing the end of the military organization that supported the Polish government-in-exile located in London.[41]
On 20 August, 1944, Romanians formed a new government which sided with the Soviets and thus allowed them to pass through. They moved into Bulgaria and Yugoslavia. Germany began to move its forces out of Yugoslavia and Greece.[38] The Finns defeated the Soviets at the Battle of Tali-Ihantala in late June and early July 1944. The battle likely convinced Stalin that conquering Finland was not worth the cost,[42] and the Moscow Armistice was signed on 19 September 1944. The Finns agreed to remove all German troops from Finnish territory.[43] On 20 October, Belgrade was liberated. Meanwhile, the Soviets reached Hungary. On 4 November, they reached Budapest, which was greatly defended. A siege began which lasted for months.[38]

At the beginning of 1945, Germany unsuccessfully attempted to take back Budapest. On 12 January, the Soviets launched the Vistula–Oder offensive, crossing the Vistula river at Sandomierz. On the 14th, the armies of Zhukov and Konstantin Rokossovsky joined the offensive, greatly expanding its size. Warsaw was isolated and liberated on the 17th.[38] Also on the 17th, those in the Auschwitz-Birkenau concentration camp who were still healthy were told to march west into more fortified German territory.[44]
Rokossovsky then moved into East Prussia. By 26 January, 1945, he reached the Baltic Sea, isolating all German forces east of Danzig. Meanwhile, Ivan Konev's forces reached the Oder river, isolating the Germans in Upper Silesia. On the 27th, the Soviets liberated those were left behind at Auschwitz.[44] Zhukov went through the corridor between the Vistula and Warta rivers and reached Brandenburg in Germany on 30 January. The Germans at this point benefited from a smaller front, meaning there was less to defend, but they were being attacked on both the western and eastern fronts. On 13 February, the Siege of Budapest ended, and the Soviets captured the city.[38]
Effects of the Eastern Front
[edit]More Soviet citizens died during World War II than those of all other European countries combined. Nazi ideology considered Slavs to be "subhuman" and German forces committed ethnically targeted mass murder. Civilians were rounded up and burned alive or shot in squads in many cities conquered by the Nazis. At least 27 million civilians and military personnel perished during the war.
8 million Red Army troops died facing the Germans and their allies on the Eastern Front. The Axis forces themselves had lost over 6 million troops, whether by combat or by wounds, disease, starvation or exposure; many others were seized as POW, about 10% of them died in the rear [45]
Lend-Lease supplies from the United Kingdom and the United States had a very important impact on Soviet military forces. Supply convoys sailed to Soviet ports that were patrolled by Nazi U-boats. Allied activities before D-Day may have tied up only a few divisions in actual fighting, but many more were forced to guard lonely coasts against raids that never came or to man anti-aircraft guns throughout Nazi-controlled Europe.
Allied invasion of occupied western Europe
[edit]
On 6 June, 1944, American, British, and Canadian soldiers began the invasion of German-occupied western Europe, named Operation Overlord. In Operation Neptune, they invaded five different beaches in the French region of Normandy - nicknamed Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno, and Sword - and established a beachhead. The allies eventually reached the French bocage, where they met intense German resistance in the Battles of Villers-Bocage and Caen. They were successful in the Battle of Cherbourg, breaking into the Cotentin Peninsula. Allied advancements disrupted the German high command. In the 20 July 1944 plot, many figures of the German high command attempted to assassinate Hitler in East Prussia; Hitler took revenge on many people in the military, and Erwin Rommel and Günther von Kluge committed suicide.[46]
In Operation Cobra, starting on 25 July, the Allies broke out of the front with Germany, and started heading toward Brittany. Hitler ordered Operation Luttich to reestablish the front, but it failed.[46] On 15 August, the Allies landed in the French Riviera in Operation Dragoon, starting an invasion of southern France.[46][47] The next day, Hitler allowed the Germans in Normandy to retreat. As they left, they were encircled by American and British spearheads at Falaise, creating the Falaise pocket. However, many Germans broke out between 16 and 19 August. By the time the Germans left Normandy, 50,000 of theirs were dead and 200,000 were taken prisoner.[46]

American General Dwight D. Eisenhower at first was going to bypass Paris during the invasion; however, on 19 August, the French in the city started a resistance against the remaining Germans, and the Allies headed towards the city. On 25 August, the Germans in Paris surrendered.[46] By September 1944, three Allied Army Groups were in line against German formations in the west. There was optimism that the war in Europe might be over by the end of the year.[47]
In mid-September, Allied forces reached the Siegfried Line, the German defensive line across western Europe.[48] The Allies made minor gains in September and October 1944, as Germans reinforced the front with new troops.[49] From 17 to 24 September, in Operation Market Garden, the Allies sent three airborne divisions to seize road bridges in the Netherlands, to be held open for the British Second Army to cross. The Allies faced serious resistance on the ground, and the operation was abandoned.[46] The Allies then began heading towards the Roer river dams to stop the Germans from destroying them and flooding the area, which would delay the Allied advance. The fastest way to the dams was through Hurtgen Forest, which was one of the most fortified areas of the Germans. The Battle of Hurtgen Forest started on 19 September, as American troops forced their way through the forest. The advance was delayed by the events of the Battle of the Bulge.[50]

The Battle of the Bulge was the last major German offensive of the war. It was an attempt to push the western Allies away from Germany. It started on 16 December. Germany's 5th and 6th Panzer Armies advanced west through the Ardennes forest, attempting to cross the Meuse river. This caught the allies by surprise.[51] The battle happened amidst extremely cold weather.[52] The Germans failed to reach the Meuse or take Bastogne, which was held by Americans. On 3 January, 1945, the western Allies began a counterattack, and by 16 January, the battle was over. The Allies suffered 75,000 casualties, and the Germans 120,000.[51] Afterwards, German forces were not resupplied to the front in great numbers.[53] This depletion of manpower stopped any chances of German large-scale resistance to the Allied invasion.[51] In early February, the Battle of Hurtgen Forest continued, and the Allies captured the desired dams. The battle cost 33,000 American casualties.[50]
In early March 1945, Allied troops began assaults to help them cross the Rhine. This allowed them to continue the invasion of Germany and encircle German forces in the Ruhr region. On 7 March, at the Battle of Remagen, the Ludendorff Bridge spanning the Rhine at Remagen was attacked by the Germans, and its foundation collapsed, but the bridge ultimately sat intact over the river. This allowed the U.S. to establish a bridgehead on the other side. All four U.S. armies in Western Europe went over the Rhine in the next few weeks; the First and Ninth Armies encircled 300,000 German soldiers in the Ruhr pocket, while the Third and Seventh Armies continued on towards central and southern Germany. German officer Walter Model dissolved the army inside the Ruhr pocket, and the 300,000 were taken as prisoners of war.[53][54][55]
End of the war in Europe
[edit]Starting in January 1945, Hitler remained in Berlin at the Chancellery and its bunker, canceling a plan to lead a resistance in southern Germany as the Soviets closed in on Berlin.[56] On 27 April, 1945, as Allied forces closed in on Milan, Mussolini was captured by Italian Partisans. He was trying to flee Italy to Switzerland and was travelling with a German anti-air battalion. On 28 April, Mussolini and several of the other fascists captured with him were taken to Giulino di Mezzegra and executed by firing squad.[57]

In April and May 1945, the Allies liberated the concentration camps of Buchenwald, Dachau, Dora-Mittelbau, Flossenburg, Mauthausen, Ravensbruck, Sachsenhausen, and Stutthof.[58] The Battle of Berlin began on 20 April as the Soviets encircled the city and began shelling the last pockets of resistance with large amounts of artillery.[56][59] Hitler became exhausted and began to accept Germany's inveitable failure and the idea of him committing suicide. In his last will and testament, he appointed Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz as the new head of state and Joseph Goebbels as chancellor. On 30 April, Adolf Hitler, with his wife of one day, Eva Braun, committed suicide in his bunker.[56] The German garrison commander, General Helmuth Weidling, then surrendered. Individual German troops continued fighting while the surrendered troops were captured and committed suicide.[59]
The Battle of Berlin ended on May 2. It caused 100,000 Soviet casualties and an unknown number of German deaths.[59] On May 4, Karl Dönitz went to British officer Bernard Montgomery's headquarters in Hamburg and surrendered the German forces in northern Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands. On 7 May, Eisenhower accepted Germany's unconditional surrender of all their forces, which went into effect the next day.[60] Norway was thus liberated.[61] 8 May was Victory in Europe Day, and celebrations were had around the world.[60] The Russian Federation celebrates 9 May as Victory Day.[62] In northern Italy, anti-fascist parties formed a new national government which was led by Ferruccio Parri.[63] On 5 June, 1945, the Allies signed the Berlin Declaration, which formally took over the supreme authority of Germany, bringing about the end of Nazi Germany.[64]
Aftermath
[edit]
39 million people died in the European theatre.[65] At the Potsdam Conference of 17 July to 2 August, the Allies formally agreed to many of the ideas considered at the Yalta Conference. Germany, Austria, and specifically Berlin and Vienna were all divided into four regions each occupied by the U.S., U.K., France, and the Soviet Union. The countries used the "Five Ds" when governing these regions: "demilitarization, denazification, democratization, decentralization, and deindustrialization."[66] In the Nuremberg trials of 1945 to 1946, many officials of the Nazi high command were tried for war crimes, crimes against the peace, and crimes against humanity.[67] European cities such as Berlin, Prague, and Dresden, had been destroyed, and many died during the abnormally strong winter later that year. The U.S. paid billions of dollars to rebuild Europe in the Marshall Plan.[68] The Cold War started as the capitalist and communist former Allied states began fighting for control over the new global order.[69]
See also
[edit]- European–African–Middle Eastern Campaign Medal
- Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II
- Pacific War
| Atlas of the World Battle Fronts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 1943-07-01 |
 1943-11-01 |
 1944-07-01 | |
 1944-09-01 |
 1944-12-01 |
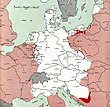 1945-03-01 |
|
Notes
[edit]- ^ From 1941
- ^ From 1941
- ^ To 1940
- ^ From 1940 to 1944
- ^ From 1944
- ^ From 1943
- ^ From 1942
- ^ The official designation of these countries under the 1947 Paris Peace Treaties[1]
- ^ Until the Armistice of Cassibile, 8 September 1943
- ^ Until King Michael's Coup, 23 August 1944
second Axis power in Europe from 8 September 1943[2] - ^ German occupation from 19 March 1944
- ^ Until 17 August 1944[3]
- ^ 25 June 1941–19 September 1944
- ^ From 23 September 1943
- ^ Vichy officially pursued a policy of armed neutrality and conducted military actions against armed incursions from both Axis and Allied belligerents. The cease fire and pledging of allegiance to the Allies of the Vichy troops in French North Africa during Operation Torch convinced the Axis that Vichy could no longer be trusted to continue this policy, so they invaded and occupied the French rump state in November 1942. Collaborationist units, such as the Milice, continued to fight alongside German troops against French Resistance fighters until the liberation of France in 1944.
- ^ Although Germany surrendered to the Allies on 8 May, the fighting continued insignificantly until 25 May.
- ^ Ellis:
- Danish: no figures;
- Norwegian: 2,000 killed or missing with no information provided on those wounded or captured;
- Dutch: 2,890 killed or missing, 6,900 wounded, with no information provided on those captured;
- Belgian: 7,500 killed or missing, 15,850 wounded, and 200,000 captured;
- French: 120,000 killed or missing, 250,000 wounded, and 1,450,000 taken prisoner;
- British: 11,010 killed or missing, 14,070 wounded (only those who were evacuated have been counted), and 41,340 taken prisoner.[10][11]
- ^ Ellis's numbers:
- American: 109,820 killed or missing, 356,660 wounded, and 56,630 captured;
- British: 30,280 killed or missing, 96,670 wounded, 14,700 captured;
- Canadian: 10,740 killed or missing, 30,910 wounded, 2,250 captured;
- French: 12,590 killed or missing, 49,510 wounded, 4,730 captured;
- Pole: 1,160 killed or missing, 3,840 wounded, 370 captured.[12] Thus according to Ellis' information, the Western Allies incurred 783,860 casualties.
- According to a post-war US Army study using war records, the army and army air forces of the United States suffered 586,628 casualties in western Europe, including 116,991 killed in action and 381,350 wounded, of whom 16,264 later died of their wounds.[13][page needed]
- ^ 43,110 Germans killed or missing, 111,640 wounded, no information is provided on any who were captured. Italian losses amounted to 1,250 killed or missing, 4,780 wounded, and no information is provided on any who were captured.[10]
- ^ Total German casualties between September 1939 to 31 December 1944, on the Western Front for both the army, Waffen SS, and foreign volunteers amounts to 128,030 killed, 399,860 wounded. 7,614,790 were held in POW camps by early June of 1945 (including 3,404,950 who were disarmed following the surrender of Germany).[12] See also: Disarmed Enemy Forces
- ^ All totals listed only include direct deaths due to military activity and crimes against humanity, including the Holocaust.[17]
Germany: 910,000. 410,000 in Allied strategic bombing, 300,000 in the Holocaust not including Austrian civilian deaths or deaths from the Nazi T4 program.[18] Counting the Aktion T4 program adds 200,000+ deaths to the total.[19]
France: 390,000. Includes 77,000 French Jews in the Holocaust.[20]
Netherlands: 187,300. Includes 100,000 Dutch Jews in the Holocaust.[21]
Belgium: 76,000. Includes 27,000 Belgian Jews in the Holocaust.[22]
United Kingdom: 67,200. Mostly died in German bombing.[23]
Norway: 8,200.[24] Includes 800 Norwegian Jews in the Holocaust.
Denmark: 6,000.[25]
Luxembourg: 5,000. Includes 2,000 Luxembourgish Jews.[26] - ^ The other main theatre of operations was the Pacific War.
- ^ All German forces were to cease operations on 23:01 hours Central European time on 8 May 1945, which was already 9 May in Moscow and other parts of the USSR; therefore 9 May was considered to be the end of the war in the Soviet Union and still is in its successor states
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ Claus Kreß, Robert Lawless, Oxford University Press, 2020, Necessity and Proportionality in International Peace and Security Law, p. 450
- ^ David Stahel, Cambridge University Press, 2018, Joining Hitler's Crusade, p. 78
- ^ Robert Bideleux, Ian Jeffries, Routledge, 2007, The Balkans: A Post-Communist History, p. 84
- ^ Frieser, Karl-Heinz (2013)The Blitzkrieg Legend. Naval Institute Press
- ^ MacDonald 2005, p. 478.
- ^ a b Glantz & House 2015, pp. 301–303.
- ^ Overmans, Rüdiger (2004). Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg (in German). München: Oldenbourg. p. 215.
- ^ Total German soldiers who surrendered in the West, including 3,404,950 who surrendered after the end of the war, is given as 7,614,790. To this must be added the 263,000–655,000 who died, giving a rough total of 8 million German soldiers having served on the Western Front in 1944–1945.Ellis 1993, p. 256
- ^ Regio Esercito: The Italian Royal Army in Mussolini's Wars, 1935–1943, Patrick Cloutier, p. 211.
- ^ a b Ellis 1993, p. 255.
- ^ MacDonald 2005, p. 478: "Allied casualties from D-day to V–E totaled 766,294. American losses were 586,628, including 135,576 dead. The British, Canadians, French, and other allies in the west lost slightly over 60,000 dead".
- ^ a b Ellis 1993, p. 256.
- ^ U.S. Army Casualties in World War II 1951.
- ^ Vadim Erlikman, Poteri narodonaseleniia v XX veke: spravochnik. Moscow 2004. ISBN 5-93165-107-1; Mark Axworthy, Third Axis Fourth Ally. Arms and Armour 1995, p. 216. ISBN 1-85409-267-7
- ^ George C Marshall, Biennial reports of the Chief of Staff of the United States Army to the Secretary of War : 1 July 1939 – 30 June 1945 Washington, DC : Center of Military History, 1996. p. 202 Archived 1 May 2017 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ a b
- Rüdiger Overmans, Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg. Oldenbourg 2000. ISBN 3-486-56531-1, "German military deaths to all causes EF". Archived from the original on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- Richard Overy The Dictators: Hitler's Germany and Stalin's Russia (2004), ISBN 0-7139-9309-X[page needed]
- Italy:
- Ufficio Storico dello Stato Maggiore dell'Esercito. Commissariato generale C.G.V. . Ministero della Difesa – Edizioni 1986
- Romania: Krivosheev 2001, Tables 200–203.
- Hungary: Krivosheev 2001, Tables 200–203.
- Hungarian wounded: Clodfelter 2017, p. 527.
- Soviet volunteer deaths:
- Percy Schramm Kriegstagebuch des Oberkommandos der Wehrmacht: 1940–1945: 8 Bde. ISBN 9783881990738 pp. 1508–1511
- German prisoners: Krivosheev 2001, Table 198.
- ^ Niewyk, Donald L. The Columbia Guide to the Holocaust, Columbia University Press, 2000; ISBN 0-231-11200-9, p. 421.
- ^ Statistisches Jahrbuch für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland 1960 Bonn 1961 p. 78
- ^ Bundesarchiv Euthanasie" im Nationalsozialismus, bundesarchiv.de; accessed 5 March 2016.(German)
- ^ Frumkin 1951, pp. 58–59.
- ^ "Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) Netherlands" (PDF). Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ Frumkin 1951, pp. 44–45.
- ^ Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2013–2014, page 44.
- ^ Frumkin 1951, p. 144.
- ^ "Hvor mange dræbte danskere?". Danish Ministry of Education. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ Frumkin 1951, p. 59.
- ^ Krivosheev 1997.
- ^ Massari, Ivano (18 August 2015). "The Winter War – When the Finns Humiliated the Russians". War History Online. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ [1] Archived 27 December 2005 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Isolation of the Revolution Archived 2006-08-26 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bojan Pancevski Dresden bombing death toll lower than thought, The Daily Telegraph, 3 October 2008.
- ^ Kate Connolly, Panel rethinks death toll from Dresden raids, The Guardian, 3 October 2008.
- ^ Landeshauptstadt Dresden (1 October 2008). "Erklärung der Dresdner Historikerkommission zur Ermittlung der Opferzahlen der Luftangriffe auf die Stadt Dresden am 13./14. Februar 1945" (PDF). Landeshauptstadt Dresden. Retrieved 13 February 2010.
- ^ Amnon Sella. 'Barbarossa': Surprise Attack and Communication. Journal of Contemporary History, Vol. 13, No. 3, (Jul., 1978), pp. 555–583.
- ^ a b c d e "Battle of Stalingrad | History, Summary, Location, Deaths, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 15 August 2024. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ a b c "Battle of Kursk | Eastern Front, German Offensive, Soviet Counterattack | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 21 August 2024. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ a b c "The Battle of Kursk: the largest tank battle in history". Sky HISTORY TV channel. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f "Eastern Front | World War II, Definition, Battles, & Casualties | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 13 September 2024. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ a b "Operation Bagration | Description & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ "Liberation of Nazi Camps". encyclopedia.ushmm.org. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ "Warsaw Uprising | Summary, Dates, & Monument | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 7 August 2024. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ Mcateer, Sean M. (2009). 500 Days: The War in Eastern Europe, 1944–1945. Dorrance Publishing. ISBN 9781434961594. Archived from the original on 29 December 2015.
- ^ "Finland declares war on Germany | March 3, 1945". HISTORY. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ a b "The Shocking Liberation of Auschwitz: Soviets 'Knew Nothing' as They Approached". HISTORY. 6 May 2024. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ "Россия и СССР в войнах XX века – Потери вооруженных сил" (in Russian). 22 July 2010. Archived from the original on 22 July 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f "Normandy Invasion | Definition, Beaches, Map, Photos, Casualties, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 9 September 2024. Retrieved 12 September 2024.
- ^ a b Tucker-Jones, Anthony (2019). D-Day 1944 : The Making of Victory. Cheltenham, UK: The History Press. p. 304. ISBN 978-0750988032.
- ^ "Hürtgen Forest". encyclopedia.ushmm.org. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ "Battle of the Bulge | Summary, Commanders, & Significance | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ a b "Hürtgen Forest". encyclopedia.ushmm.org. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ a b c "Battle of the Bulge | Summary, Commanders, & Significance | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ Simons, Paul (16 December 2014). "Weather eye: the Battle of the Ardennes". www.thetimes.com. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ a b "Death in the West: The Battle of the Ruhr Pocket". The National WWII Museum | New Orleans. 16 April 2020. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ "The Rhine Crossings in World War II". encyclopedia.ushmm.org. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Encircling the Ruhr". encyclopedia.ushmm.org. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ a b c "Adolf Hitler - Nazi Leader, WW2, Germany | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 23 September 2024. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Death of the Duce, Benito Mussolini". The National WWII Museum | New Orleans. 28 April 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Liberation of Nazi Camps". encyclopedia.ushmm.org. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ a b c "Battle of Berlin | Description & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ a b "What You Need To Know About VE Day". Imperial War Museums. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Norway". encyclopedia.ushmm.org. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Russia celebrates victory in World War II as Putin accuses the West of fueling global conflicts". AP News. 9 May 2024. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Italy - Post-WWII, Renaissance, Culture | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 24 September 2024. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ^ "Avalon Project – Declaration Regarding the Defeat of Germany and the Assumption of Supreme Authority by Allied Powers; June 5, 1945". avalon.law.yale.edu. Retrieved 25 December 2022.
- ^ Kesternich, Iris; Siflinger, Bettina; Smith, James P.; Winter, Joachim K. (1 March 2014). "The Effects of World War II on Economic and Health Outcomes across Europe". The review of economics and statistics. 96 (1): 103–118. doi:10.1162/REST_a_00353. ISSN 0034-6535. PMC 4025972. PMID 24850973.
- ^ "Potsdam Conference | Facts, History, & Significance | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 5 September 2024. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Holocaust - Jewish Resistance, Nazi Oppression, Persecution | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 24 September 2024. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "The Cost of Victory". The National WWII Museum | New Orleans. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Cold War | Summary, Causes, History, Years, Timeline, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 24 September 2024. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
Works cited
[edit]- Clodfelter, Micheal (2017). "The Toll of World War II". Warfare and Armed Conflicts: A Statistical Encyclopedia of Casualty and Other Figures, 1492–2015 (4th ed.). Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Co. ISBN 978-0-7864-7470-7.
- Ellis, John (1993). The World War II Databook: The Essential Facts and Figures for all the combatants. BCA. ISBN 978-1-85410-254-6.
- Frumkin, Gregory (1951). Population Changes in Europe Since 1939. Geneva: Allen & Unwin.
- Glantz, David M.; House, Jonathan M. (2015). When Titans Clashed: How the Red Army Stopped Hitler. Modern War Studies (2nd ed.). University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-2121-7.
- Keegan, John (1989). The Second World War. Hutchinson. ISBN 0-09-174011-8.
- Krivosheev, G. I. (1997). Soviet Casualties and Combat Losses. Greenhill. ISBN 1-85367-280-7.
- Krivosheev, G. I. (2001). Rossiia i SSSR v voinakh XX veka: Poteri vooruzhennykh sil; statisticheskoe issledovanie (in Russian). OLMA Press. ISBN 5-224-01515-4.
- MacDonald, C. (2005). The Last Offensive: The European Theater of Operations. University Press of the Pacific.
- Office of the Adjutant General, U.S. Army (25 June 1953). U.S. Army Battle Casualties and Non-battle Deaths in World War II: Final Report (Report). CSCAP (OT) 87 – via HyperWar Foundation.
- Overy, Richard (1995). Why the Allies Won. Pimlico. ISBN 0-7126-7453-5.
Further reading
[edit]- Churchill, Winston. The Second World War. 6 volumes, 1948–1953
- Hanson, Davis Victor (2017). The Second World Wars: How the First Global Conflict Was Fought and Won. Basic Books.
- Lee, Loyd E., ed. (1997). World War II in Europe, Africa, and the Americas, with General Sources: A Handbook of Literature and Research. Westport, CN / London: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-29325-2.
- Murray, Williamson; Millett, Allan R. (2000). A War to Be Won: Fighting the Second World War. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-00163-X.
- Powaski, Ronald E. (2003). Lightning War: Blitzkrieg in the West, 1940. John Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-39431-0.
- Powaski, Ronald E. (2016). Lightning War: Blitzkrieg in the West, 1940. Book Sales. ISBN 978-0-7858-2097-0.
- Weinberg, Gerhard L. (2005). A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-44317-2.

